 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
| 제품번호 | 종 | 제품 설명 | 구조 | 순도 | 특징 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
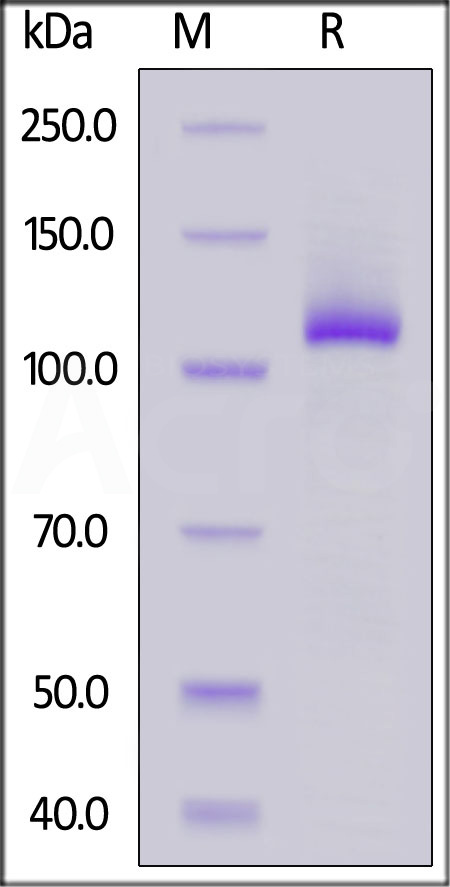
| FG1-H5254 | Human | Human FGL1 (64-312) Protein, Fc Tag | 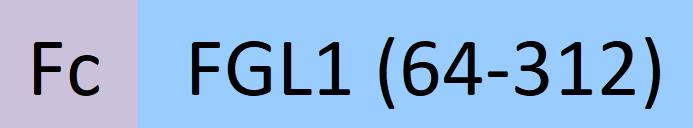 |
|
|
| FG1-M5258 | Mouse | Mouse FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag | 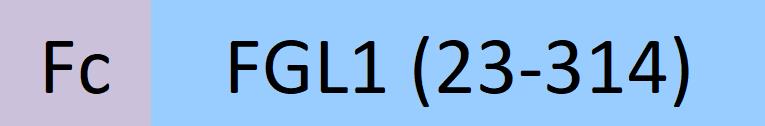 |

|
|
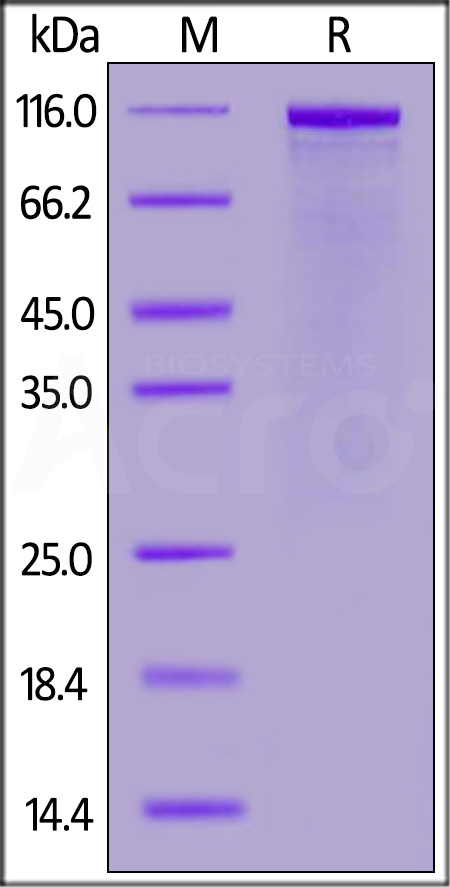
| FG1-H82F6 | Human | Biotinylated Human FGL1 (64-312) Protein, Avitag™,Fc Tag (high sensitivity) |

|
||
| FG1-C5250 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FGL1 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc Tag | 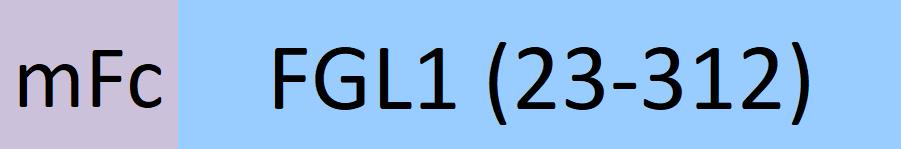 |

|
|
| FG1-C5269 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag |  |

|
|
| FG1-H82Ey | Human | Biotinylated Human FGL1 Protein, His,Avitag™ (recommended for biopanning) |  |

|
|
| FG1-H82F4 | Human | Biotinylated Human FGL1 Protein, Avitag™,Fc Tag |  |
|
|
| FG1-H52Hy | Human | Human FGL1 Protein, His Tag | 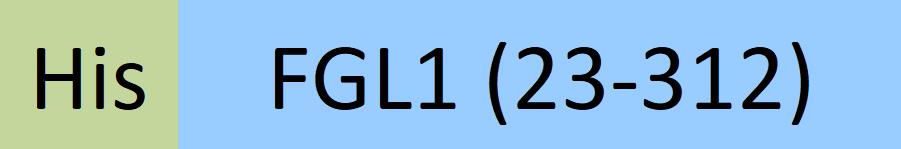 |

|
|
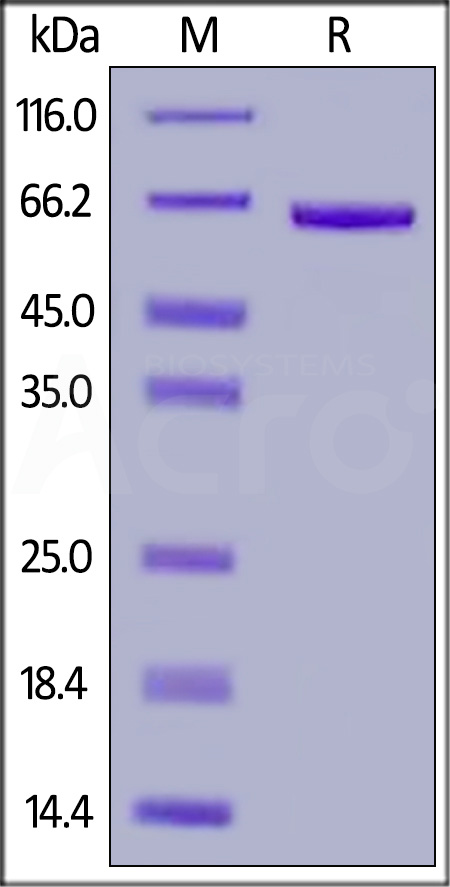
| FG1-H5258 | Human | Human FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag | 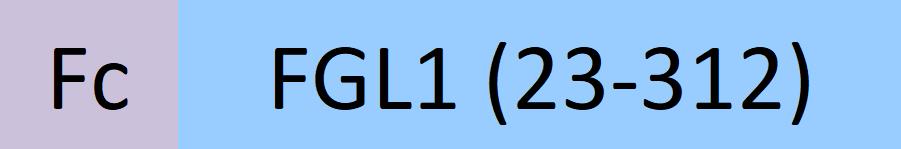 |

|

FACS assay shows that Biotinylated Human FGL1 (64-312), Avitag,Fc Tag (Cat. No. FG1-H82F6) can bind to 293T cells overexpressing human LAG3. The concentration of Human FGL1 is 3 μg/ml (Routinely tested).
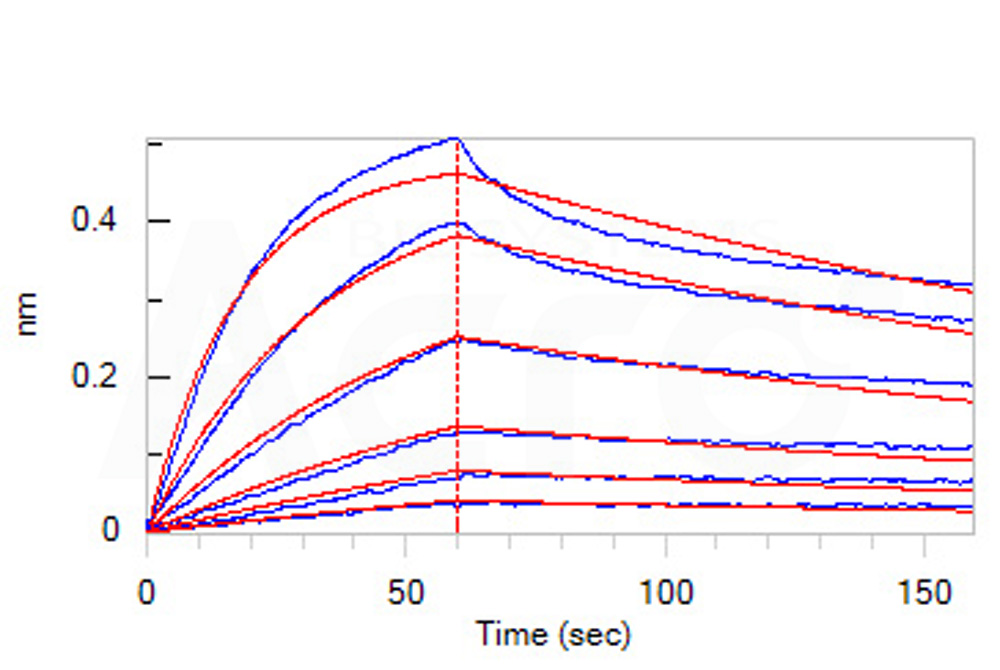
Loaded Biotinylated Human FGL1 (64-312), Avitag,Fc Tag (Cat. No. FG1-H82F6) on SA Biosensor, can bind Human LAG-3, Fc Tag (HPLC-verified) (Cat. No. LA3-H5255) with an affinity constant of 3.78 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (Routinely tested).
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
