Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs)--A Novel Approach to Modeling Neurodegeneration
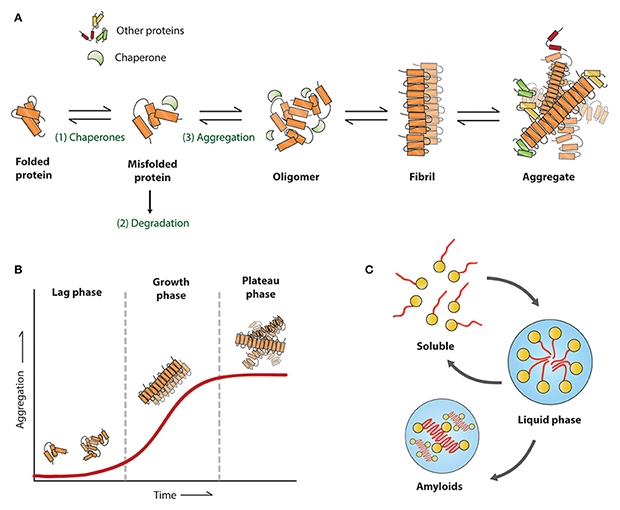
Protein aggregation is a major pathological feature of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Huntington's disease (HD). Under pathological conditions, Tau, Amyloid beta, alpha-synuclein, TDP-43, Huntingtin and other proteins integrate into a wide array of undesirable structures, ranging from oligomers and prefibrillar assemblies to highly ordered aggregates. The fibrillar structure represents a rapid growth phase of protein aggregation as these fibrils are “active” and rapidly recruit monomers for elongation. In additions, these fibrils randomly break into shorter fragments that could act as “seeds”, which transmits to other cells and independently recruits monomers to form novel fibrils. Pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) are in vitro formed active fibrils that have this "seeding" activity and are capable of continuously recruiting soluble endogenous pathological proteins to form aggregates and finally induce neurodegenerative pathologies.
The establishment of reliable disease models is crucial for discovering the pathological mechanisms, evaluating the efficacy of therapeutic interventions, and assessing the safety of drug candidates. Compared with traditional disease modeling approaches, PFFs induced pathology does not depend on gene editing, chemical or physical damage, and it can better mimic naturally occurring pathological states processes. Therefore, PFFs is a novel approach to modeling neurodegenerative diseases.
PFFs could be generated from monomers either by incubating at 37°C and shaking, or by heparin induction. Quality control and precise initial preparation are important for successful experiments. One important aspect of successful induction of PFFs is the use of high-quality monomer with high purity, high concentration and correct conformation. Meanwhile, since the application of PFFs is cellular and animal experiments, the control of endotoxin is also an important factor. In addition, prior to the use of PFFs, PFFs should become a length of 50 nm or shorter via ultrasound to ensure the recruiting activity of PFFs as well as to facilitate the endocytosis of PFFs.
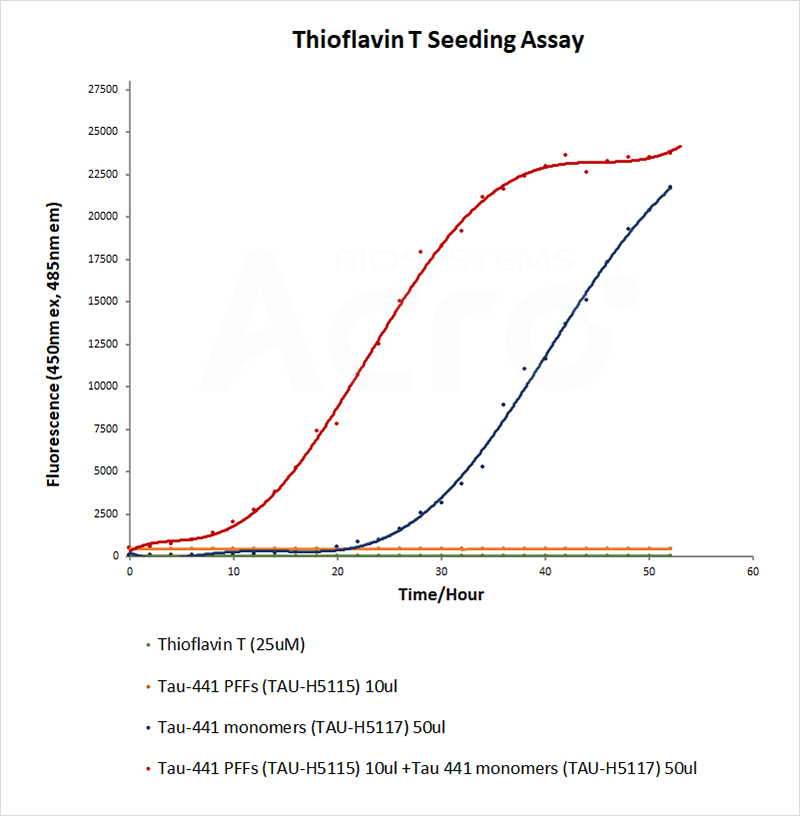
The morphology and activity of PFFs could be verified by electron microscope and thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence assay respectively. Successfully induced PFFs show fibril structure under electron microscope. ThT assay is a classic assay to detect β-sheet structures. PFFs acquire more and more β-sheet structures as they recruit monomers, and when ThT binds to the β-sheet structure, the fluorescence value increases, thus reflecting the activity of PFFs.
As the brand of ACROBiosystems that focused on neuroscience, Aneuro provides Tau-441 PFFs, alpha-synuclein PFFs, Amyloid beta PFFs, TDP-43 PFFs and SOD-1 PFFs, supporting and accelerating the establishment of reliable neurodegenerative models.
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description | Monomer Source | Expression System | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tau | TAU-H5115 | Human Tau-441/2N4R Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free | TAU-H5117 | E.coli | |
| TAU-H5116 | Human Tau-441 K18 Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free | NA | E.coli | ||
| TAU-H5113 | Human Tau-441 K18 (P301L) Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free | TAU-H5118 | E.coli | ||
| Alpha-Synuclein | ALN-H5114 | Human Alpha-Synuclein (A53T) Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free | ALN-H5116 | E.coli | |
| ALN-H5115 | Human Alpha-Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free | ALN-H5214 | E.coli |
More PFFs relevant products under development. PFFs are under development.
Leave a message
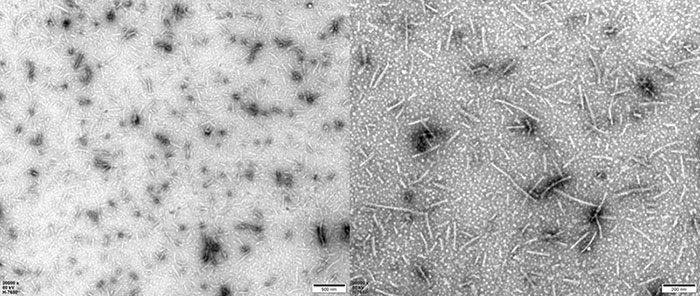
TEM of Human Tau-441/2N4R Pre-formed Fibrils Protein (Cat. No. TAU-H5115).
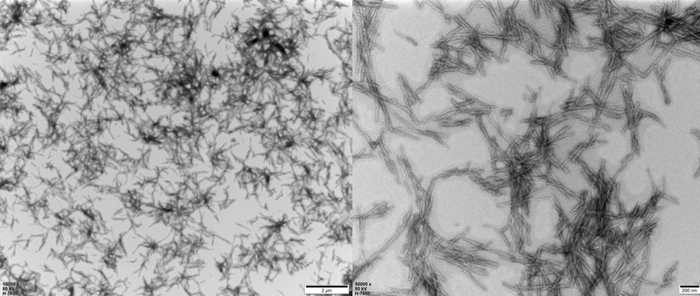
TEM of Human Tau-441 K18 (P301L) Pre-formed Fibrils Protein (Cat. No. TAU-H5113).
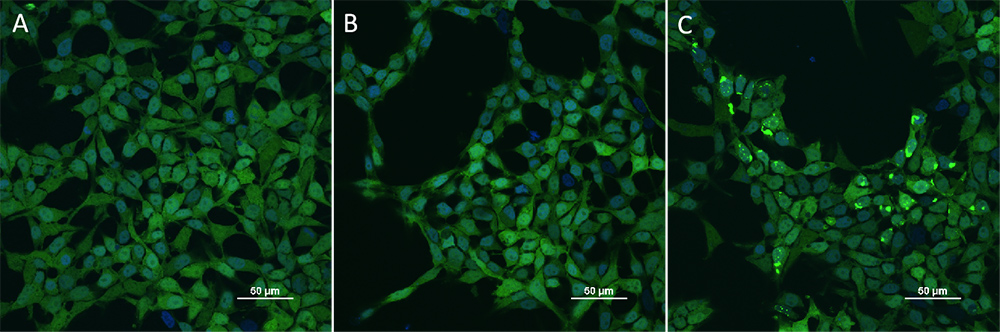
HEK293/Human Tau(GFP) Stable Cell Line were transduced with Human Tau-441 / 2N4R Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free (ThT active) (Cat. No. TAU-H5115) and Human Tau-441 / 2N4R Protein, Tag Free (MALS verified) (Cat. No. TAU-H5117) respectively. The fluorescence of GFP-Tau (Green) and DAPI (Blue) were detected by confocal microscope. A. Lipo2000 transduction. B. Lipo2000 and Human Tau-441 / 2N4R Protein, Tag Free (MALS verified) transduction. C. Lipo2000 and Human Tau-441 / 2N4R Pre-formed Fibrils Protein, Tag Free (ThT active) transduction. Scale bars, 50 μm.
1. Stroo E, Koopman M, Nollen EA, Mata-Cabana A. Cellular Regulation of Amyloid Formation in Aging and Disease. Front Neurosci (2017). doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00064. PMID: 28261044; PMCID: PMC5306383.
2. Guo JL, Lee VM. Seeding of normal Tau by pathological Tau conformers drives pathogenesis of Alzheimer-like tangles. J Biol Chem (2011). doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.209296. Epub 2011 Mar 3. PMID: 21372138; PMCID: PMC3083182.
3. Sanders D W, Kaufman S K, DeVos S L, et al. Distinct tau prion strains propagate in cells and mice and define different tauopathies[J]. Neuron, 2014, 82(6): 1271-1288. doi: 10. 1016 / j. neuron. 2014. 04.047.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.