Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> Liver-related Solutions & Services
Explore our ready-to-use liver organoids, cells, kits, and services. Learn about our robust ready-to-use organoid and differentiation kits that undergo rigorous quality control, including cell viability assays, and enzyme activity testing. Our reliable services include liver organoid differentiation, disease modeling, and drug testing cater to the specific research needs.
Traditionally, drug hepatotoxicity evaluations rely on animal studies that have limitations such as high costs, long durations, and ethical concerns. However, liver organoids enable an in vitro simulation of drug toxicity effects, providing a rapid and accurate assessment for drug safety. Moreover, liver organoids can mimic the pathogenesis of various liver diseases such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and liver cancer, aiding in early diagnosis and monitoring, as well as exploring treatment options.
Liver Organoids
Liver organoids are a miniaturized, in vitro version of the liver that is derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These organoids are designed to have a similar cellular composition and architecture to the liver, reflecting human-specific drug metabolism. As such, liver organoids are critical tools for researchers, enabling personalized drug screening and replicating key hepatic functions while mimicking the physiological architecture of the liver.

Drug Screening
Drug Screening
Liver organoids derived from human cells mimic native liver tissue and have functional properties, enabling their application in a scalable, high-throughput drug screening including efficacy and toxicity assessments.

Liver Development Research
Liver Development Research
By utilizing liver organoids, researchers can investigate various biological events during liver development, such as cell differentiation, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. These studies contribute significantly to uncovering the molecular mechanisms.

Personalized Medicine
Personalized Medicine
Defining a treatment strategy is the foundation of personalized medicine. Personalized medicine utilizing liver organoids has the potential to screen for therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects on an individual scale.
Liver organoids and differentiation kits are available to support high-throughput differentiation of liver organoids from iPSCs.
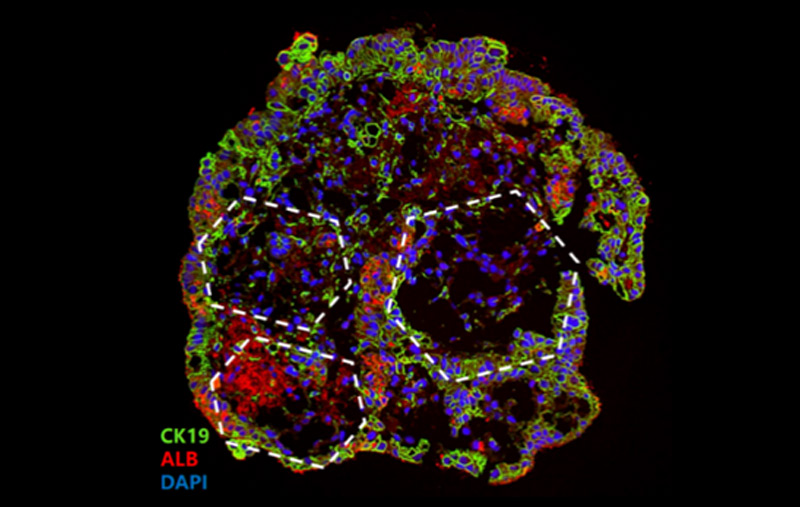
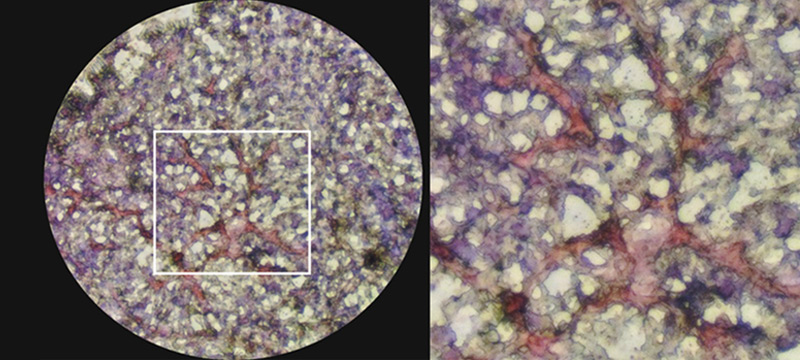
Bile duct epithelial marker (CK19) revelas typical hexagonal structure of hepatic lobule demonstrating a sigificant level of maturity and functionality similar to native liver tissue.
| Cat. No. | Description |
| CIPO-RWL005K | Ready-to-use Human iPSC-Derived Liver Organoids |
| RIPO-RWM009K | Human iPSC-Derived Liver Organoid Differentiation Kit |
| RIPO-RWM010 | Human iPSC-Derived Liver Organoid Maturation and Maintenance Kit |
Liver Cells
Interested? Leave a message!
Liver Services
We utilize specific cytokines and stimuli to induce reprogramming or differentiation of iPSC or human tissue. The differentiation and maturation of organoids are identified by the expression of liver-related protein markers.
We measure the inhibition of CYP450 expression and enzyme activity under the action of the drug, since the ALB secreted into the medium also represents the liver activity.
We can help to construct the AD/PD model with PFFs and provide corresponding pathological findings and biochemical evidence. At the same time, we can also provide you with follow-up drug screening services.
Liver Case Studies
Developed using our organoid differentiation kit, iPSC-derived liver organoids were stained with Oil red. Accumulation of fatty acids in between nuclei reveal the pathological changes that mimic NASH.
References
1. Kulkeaw, K.; Pengsart, W. Progress and Challenges in the Use of a Liver-on-a-Chip for Hepatotropic Infectious Diseases. Micromachi nes 2021, 12, 842. https://doi.org/10.33 90/mi12070842.
2. akebe, T., Sekine, K., Enomura, M. et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature 499, 481–484 (2013).
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.