Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
| 제품번호 | 종 | 제품 설명 | 구조 | 순도 | 특징 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
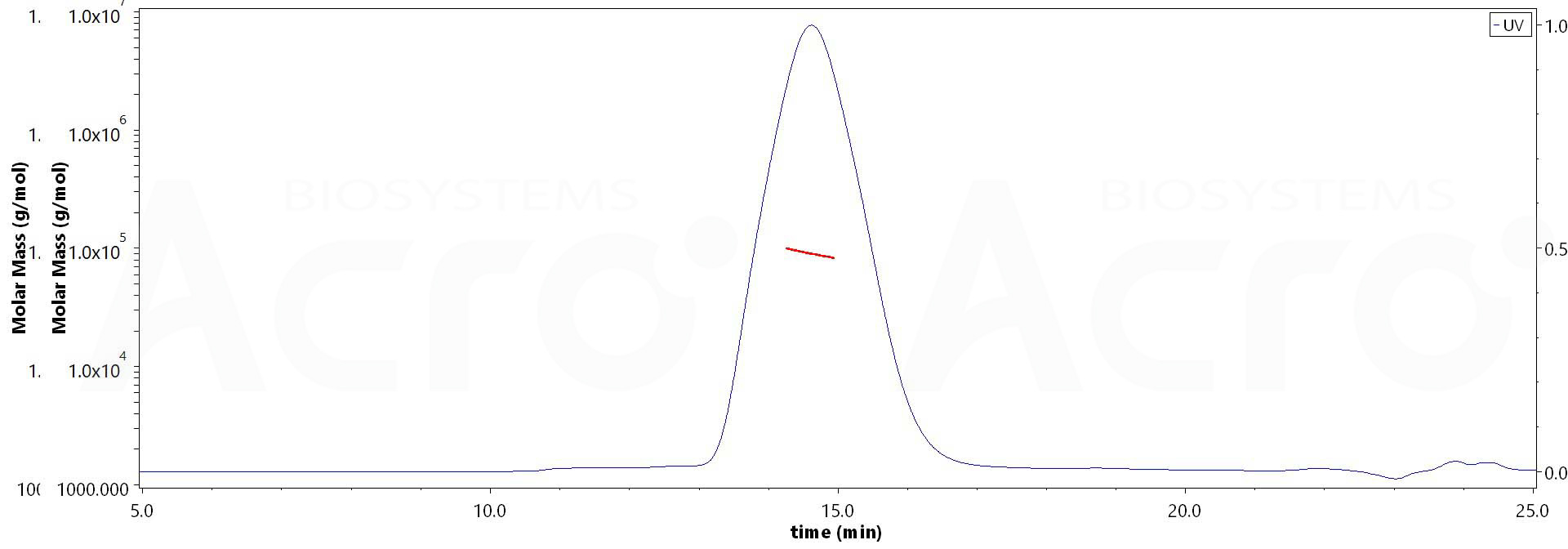
| GP0-E52H6 | Epstein-Barr virus | Epstein-Barr virus (Herpesvirus 4) EBV Glycoprotein gp350 / EBV GP350 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |  |

|
Please contact us via TechSupport@acrobiosystems.com if you have any question on this product.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.